Clarkdale: A Closer Look

Intel Clarkdale die.
While the Clarkdale architecture is derived ultimately from Nehalem, it is most similar to Lynnfield, which is likely why they share the same socket. Where Lynnfield offered only the CPU package with just an external PCIe link, Clarkdale adds the GPU on package.

Lynnfield showed us that Intel could get very aggressive with power savings, putting many parts of the CPU into deep sleep states when not in use. We saw incredibly low power usage at idle for a quad core processor, yet were still able to have class leading performance. With Clarkdale, Intel has dropped two CPU cores, 4MB of cache, and shrunk the die to 32nm. Intel seems content sticking to 2MB of L3 per CPU core even with the die shrink. This gives us a 2 core/ 4 thread part with 4MB of cache that sips power at idle, yet is a monster performer when called upon. The Integrated Memory Controller is a dual channel with official support up to 1333MHz, which is the same as Lynnfield.
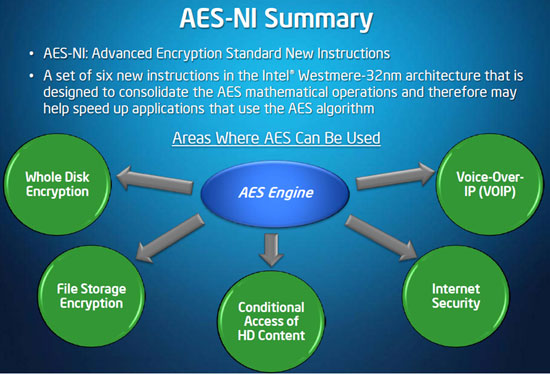
A new feature exclusive to the Westmere family is a new instruction set called AES-NI that, as the name implies, supports AES (Advanced Encryption Standard). It is 6 instructions designed to consolidate the AES mathematical operations, which can help speed up applications that use the AES algorithm. When tested in PC Mark Vantage and Sandra 2010, we see an increased performance in the Communications score for Clarkdale over Lynnfield.
There are a number of hard disk encryption applications available that make use of AES, as well as programs like 7z, WinZip, and RAR.
The biggest change with Clarkdale is the addition of the Intel HD Graphics processor on package with the CPU. Some of the highlights are:
- Displaying to multiple monitors, including dual HDMI and DisplayPort
- Run Windows 7 Aero with full effects
- Process Dual video decode (Picture in Picture playback) and Dual audio streams
- Provide Dolby True HD, DTS-HD Master Audio from Blu-ray and HD-DVD
- Mainstream gaming
While many of these are great features for an on-board GPU, anyone wanting to try and play a recent PC game at a resolution greater than 800x600 on low detail should probably look for an add-in graphics card. Intel HD Graphics support WDDM 1.1 and is a DirectX 10 part. It offers full decoding for H.264, VC-1, and MPEG2. It is also optimized for Flash and Silverlight.
The Intel HD Graphics processor can allocate up to 1.7GB of system memory thanks to a technology called Dynamic Video Memory Technology (DVMT). The older G-Series in LGA-775 could only allocate up to 768MB. The amount of video memory allocated depends upon the amount requested by the operating system. When the memory is no longer required, it is returned to the operating system for use by other applications or system functions.


